Economics is the social science that acknowledges the consumption, production and transfer of wealth within the country.
Economics is the normative science which deals with the interaction of people with the resources. It is the study of human behaviour which describes the relationship between limited resources and unlimited wants.
Economics is mainly divided into two groups- Macroeconomics and Microeconomics. The difference between macro and micro economics is a vast subject.
As stated, Economics is about production, consumption and distribution of goods and services within the country; it comprises both micro and macro Economics.
To understand the difference between macro and micro economics, it is important to study them individually.
Microeconomics
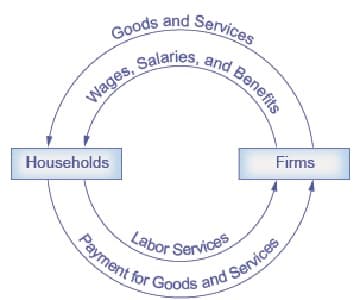
Microeconomics is the part of economics that deals with the allocation, production and consumption of resources at the individual level.
Microeconomics is the study that involves the peoples, households and companies’ decision-making process. It focuses on choices made by individuals that affect the prices of goods and services.
Microeconomics is primarily known as the study of markets. As the interactions of peoples involve the selling and buying of goods and services, which mainly occurs in market t, it is referred to as the study of the market.
Microeconomics is generally a bottom-up approach to scrutinize the interactions within the market. The prime role of Microeconomics is to help people and companies to increase and maximise their profit.
Microeconomics is superiorly concerned with the supply and demand in the market. It focuses on stability and maintaining equilibrium between the prices and capacity of goods and services.
Study of microeconomics is significant for manufacturers as it helps them to get an idea of the needs of consumer and margin of the production.
Microeconomics involves various other economics such as labour economics, political economics, public economics, financial economics, industrial economics, health economics, urban economics and much more.
Microeconomics studies consumer behaviour as an individual. It also includes demand and service of labours which includes determinants of labour wages, labour markets and demand.
Examples of microeconomics:
1)Individual demand and supply
2)Price of products
3)Labour wages
Macroeconomics

Macroeconomics is part of economics that deals with production, consumption and distribution of goods and services as a whole.
Macro means large. The name suggests that is the study concerned about large firm such as a nation.
Macroeconomics is the study of decision-making, the structure of the whole country. The decisions taken affect the whole country.
Macroeconomics focuses on making policies, applying them and maintain the factors influencing the economic condition of the country.
Macroeconomics follows a top-down approach. It is strategies and executed on a massive scale. Macroeconomics examines entire industries and economics rather than the individual.
The prime motive of macroeconomics is to increase overall GDP that is Gross Domestic Product of a country. It supervises factors such as inflation, unemployment, poverty, per capita income etc.
Macroeconomics helps to study long-run economic growth of the country. It also comprises of balance between export and import of goods and services within the country.
Macroeconomics helps in making policies such as Fiscal policy and Monetary policy, which help in stabilizing the prices and interests’ rate.
Macroeconomics helps to study and solve reasons for the unemployment and inflation within the country. It helps to generate an equitable distribution of wealth and income within economic classes.
Macroeconomics also helps to understand and supervise international trade and globalisation.
Macroeconomics studies the reasons for the difference in living standards of different countries and surveys overall growth of the country.
Examples of macroeconomics:
1)National Income
2)Revenue
3)Aggregate demand etc.
Difference between macro and micro economics
There are various aspects and parameters in which one can understand the difference between macro and micro economics. The following lists describe the difference between macro and micro economics in detail
-
Definition
The definition or meaning itself describes the difference between macro and micro economics.
Microeconomics is the study of the allocation, production and consumption of resources at the individual level. It comprises the study of a particular market segment only.
Microeconomics studies human behaviour as an individual or a company. It acknowledges the small-scale unit of the economy.
Whereas, macroeconomics is the study of deals with production, consumption and distribution of goods and services as a whole.
Macroeconomics comprises all the market segment of the country. Macroeconomics studies all the factors influencing the nation’s income and economy.
Macroeconomics is a large-scale study which includes the aggregates of the country’s economy.
Therefore, the meaning of the terms explains the prime difference between macro and micro economics.
-
Deals with
The chief difference between macro and micro economics is with what it deals with. There are various factors with whom both macro and microeconomics deal with.
Microeconomics deals with an individual’s human behaviour and decision making. It comprises of activities such as production, consumption of goods, economic welfare etc.
Microeconomics deals with factors such as demand and supply of goods and services, price of goods and products, individual income, factor pricing etc.
Whereas Macroeconomics deals with the economic behaviour of a whole. It comprises a social and economic status of the nation.
Macroeconomics deals with factors such as National income, national output, generate price levels, employment, distribution of economy etc.
Both macro and micro economics deal with different factors of the economy.
-
Motive and focus
The other main difference between macro and micro economics can be understood by acknowledging the motive and focus of both terms.
Microeconomics focuses on the distribution of resources and understanding the supply and demand of goods and services of the market. It focuses on solving the issues of individuals concerning with price.
Whereas Macroeconomics focuses on the overall economy of the country. It focuses on National income and factors influencing the economic growth of the country, such as employment and Gross Domestic Product.
-
Factors
Factors are another important aspect that helps to understand the difference between macro and micro economics.
Major factors of microeconomics are demand and supply of goods of a particular segment of the market, individual’s consumer behaviour etc.
Major factors of macroeconomics include price, aggregated demand and supply, per capita income of the country etc.
Both macro and micro economics have different factors affecting them.
-
Business application
Business application is another one of the important aspects which help us to learn the difference between macro and micro economics.
The application of economic factors and terms in business is very important.
Microeconomics is mainly applied to internal issues arising from within the company or individuals. As stated, microeconomics deals with supply and demand of goods, and there are many issues relating to it.
Internal issues such as number of products to manufacture and sell, price of every commodity, transport charges etc. are resolved by microeconomics.
Macroeconomics is mainly applied to external and environmental issues arising within the whole country. Issues relating to the economic growth of the country are resolved by macroeconomics.
External issues such as export and import of goods and services, unemployment, increasing pollution, a difference of living standards to other nation etc. are categorized under business application of macroeconomics.
Both microeconomics and macroeconomics have their application in different fields. And both help to resolves issues in their application.
-
Study
Microeconomics studies the economic interactions of a specific company or individual. Microeconomics studies human consumer behaviour and its interaction within the market.
Microeconomics studies resources allocation, cost of products, available resources etc.
Whereas Macroeconomics studies the economic interactions of the whole nation.Macroeconomics studies the Gross Domestic Product, investment patterns, production and consumption trends etc.
Macroeconomics also studies the aggregate economic factors.
Macro and micro economics both studies different aspects of economies.
-
Tracking
Tracking is another main aspect of the economy. Tracking of prices, the number of products bartered etc. are included in tracking. It can be in terms of one unit or whole units.
Microeconomies tracks the smallest products or units and their functioning. Microeconomies tracks the supply and demand trends within the market. Microeconomics also tracks the production of goods and their consumption.
Whereas, macroeconomics tracks whole aggregated units of the country or nation. Macroeconomics tracks whole of the consumption and production within the country.
Macroeconomics tracks the income of the country and net values of goods and services as well.
By tracking, one can understand the difference between macro and micro economics in a much broader manner.
-
What it provides
The difference between macro and micro economics can be well acknowledged by what facilities or services they provide.
Microeconomics offers the approx—the figure for the number of goods and services which are required within the market to get stability.
Microeconomicsprovidese the solutions to problems relating to the growth of the economy within the company or individuals.
Macroeconomics, on the other hand provides the fair distribution and consumption of goods and services within the country.
Macroeconomics offers the income trends and globalization facts which influence the economic growth of the nation.
Both macroeconomics and microeconomics provide different services to ensure economic stability.
-
Scope
Scope of both the terms is important to understand the difference between macro and micro economics.
Scope of microeconomics is limited to a single household or individual only. Microeconomics can only cover issues arising to a single firm or unit.
Microeconomics can cover issues like welfare production, demand, supply, factor pricing, product pricing, manufacturing and consumption etc.
Whereas in the case of Macroeconomics, the scope is not limited to a single firm; instead it covers issues arising to the whole country or nation.
Macroeconomics can cover issues such as national income, money, distribution, employment, price level etc.
-
Equilibrium
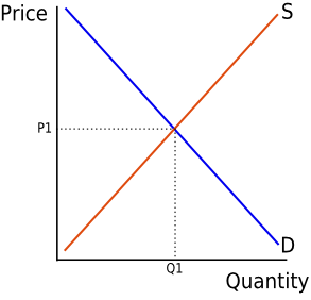
Equilibrium is the balance of point between demand and supply of goods. It is at most necessary for every market to have equilibrium.
Equilibrium ensures the profit and loss within the company or nation. Therefore, it is one of the chief aspects of the difference between macro and micro economics.
Microeconomics ensures the equilibrium at a small scale. That is, it helps a single firm to understand the balance between consumer wants and the production of goods.
Microeconomics helps the individual to maintain the demand and supply to the market.
Whereas in the case of Macroeconomics, it helps to ensure the equilibrium between the income of the country and available employment in the nation.
Macroeconomics ensures the balance of import and export of goods between different countries. It also maintains equilibrium between the needs and utilization of aggregated goods.
-
Significance
Significance is also one of the aspects of the difference between macro and micro economics.
Significance in terms of how both micro and macro economies are useful to the citizen of the country.
Microeconomics is useful as it helps to analyse the prices of production of goods. Microeconomics also helps to regulate the factors of production, which are land, labour, capital and entrepreneur.
Macroeconomics is useful as it analyses the major issues of the economy like inflation, poverty, unemployment and deflation within the country.
Macroeconomics also helps to understand the prices levels of different commodities.
-
Limitations
Every aspect has its own limitations. To understand the difference between macro and micro economics, it is important to learn its limitations.
Microeconomics is generally based on the assumption that there is full employment within the firm, which is not possible.
While making trends, we assume that all products which are produced, are consumed, which is not feasible at all. Some impractical assumptions are also taken while studying factors affecting the economy.
Whereas in the case of macroeconomics, assumptions are taken for aggregate factors which sometimes may not be true.
For example, aggregate supply and goods of a country may not rely on individuals demand and supply.
Also, assumptions are taken while aggregation may not be accurate every time.
-
Example
Examples are easier to understand. Therefore, one can learn the difference between macro and micro by acknowledging the examples.
Examples of microeconomics include consumer equilibrium, price determination of a particular product, individuals’ income, the output generated by individual firms, labour wages etc.
Examples od macroeconomics include general price level, per capita income, poverty, rate of employment, national income, national investments, aggregated demand and supply, savings of country etc.
Microeconomics and macroeconomics have their own differences and similarities. We can say that somewhere they are interdependent on one another.
For maintaining stability and balance between production, allocation and consumption, both micro and macroeconomics are equally important.
