Hey readers, I hope you are doing well, and am sending lots of hugs and positivity to all of you. So, today’s blog post is pretty much unique and scientific, as we’ll dive deep into the field of chemistry and get to know about this chemical element that is used a lot and has unique features, and that chemical element is Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution.
Well, that’s an interesting topic, and would love to talk about Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution and would love to revisit Chemistry. Guys I am not in the field of science professionally but have an interest in the field of science and technology as it’s very important and plays a major role in our daily lives. Whether you are a science student or even a commerce or art student, I think every individual should some basic knowledge about science. So, before we dive deep into this unique topic and get into the crazy world or field of chemistry, which is an integral part of the Science ecosystem, and go further, let’s understand,
What is Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution?
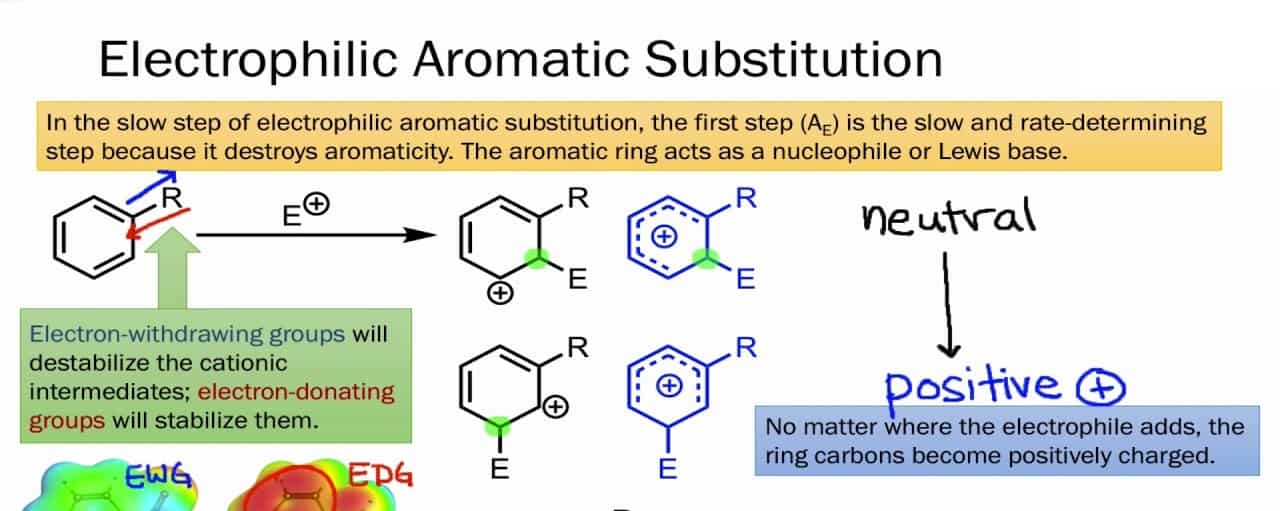
So, let’s keep it simple for people who are not from a chemistry background or for people who are not from a science background in general, basically Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution is an organic reaction in which atoms are attached to an aromatic ring and the electrophile replaces Hydrogen atoms that belong to the benzene ring with an electrophile. And that’s what the field of Chemistry is all about experimenting, testing, and processing. Isn’t it fun readers, as it really requires a great amount of knowledge and the energy to keep on working and experimenting?
I never had an experience in the field of chemistry as I was not good in academics at all when I was in school, but as I grew up, I realized how important it is to know the basics of science as the world runs on it, we need it, we thrive to know about it, and that’s how the economies around the globe work. I still regret not continuing with science as it’s just outstanding, makes you think deeper, and helps you to solve a problem and come up with the solution.
The teacher who taught me Chemistry was not at all good, and that’s the reason why the interest in science was not developed as it was just theory and not practical exposure. Anyways getting back to the topic, there are around 5 types of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reaction that has been evolved for a long time and still working in today’s time and they are as follows:-
- Aromatic Nitrate Reaction:- Basically it’s the type of reaction in which hydrogen is replaced with a nitro(NO2) group. In this type of reaction, Sulfuric acid(H2SO4) is used as a catalyst and it reacts with the nitric acid that leads to the formation of a nitronium ion, and then the nitronium ion is processed further as per the mechanism of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution.
- Aromatic Halogenation:- This is another type of reaction in which just like an Aromatic nitrate reaction, hydrogen is replaced with bromine or chloride. In this reaction process, the use of bromine or chloride gets mixed up or is used with Lewis acid, which takes a pair of electrons to form a permanent bond dipole in the Cl-Cl bond or the Br-Br bond. This reaction helps bromine or chloride to form a positive charge as the dipole makes the group of electrophilic easy enough to overcome the activation energy that is generated due to the loss of aromaticity of the benzene ring.
- Aromatic Sulfonation:- In this type of reaction, Sulfonation is processed when Hydrogen is replaced with the help of sulfonic acid(SO3). Just like the Nitrate reaction mentioned above, it’s sort of similar where an electrophilic is generated by the protonation of SO3, with H2SO4. It helps to generate a strong electrophile, and once it’s processed then the reaction follows the Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution.
- Friedel-Crafts Acylation:- This is a set of chemical reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877, and it’s distinguished into two types of reaction, one is Friedel-Crafts Acylation, and the other is Friedel-Crafts Alkylation. So, this is a type of reaction in which Hydrogen is replaced with an Acyl group(RC=O). Reagents that are used in this type of reaction are carboxylic acid halides or acyl chlorides, and even Lewis acid is used as a catalyst. It forms electrophile(generally acylium ion) by using a single pair from the chlorine of the H3C(C=O)Cl which is used in filling the open outlet of aluminum that belongs to AlCl3. The end product that is formed in the end is aryl ketone as the chlorine carbon bond becomes weak and that leads to Cl+-Al-Cl3.
- Friedel-Crafts Alkylation:- This is another type of reaction developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts. In this type of reaction, just like the previous Friedel-Crafts reaction, the Hydrogen is replaced with an Alkyl group(R). Alkyl Halide such as CH3CH2Cl is used as a reagent along with Lewis acid like AlCl3 or FeCl3 amongst others. This type of acid process can help to accelerate the further reaction by coordinating with halogen that further weakens the C-Cl bond and makes it leave the group of reaction. But one flaw of this reaction is that the product becomes more nucleophilic than the reactant and that can even lead to overalkylation.
So, these were the types of reactions of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Now let’s dive deep into the basics of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution, as it’s important in the field of chemistry to understand every basic point of every element because that’s the foundation of the subject and that’s what makes us know the details. So, there is this saying,
” The Devil lies in the details, the devil lies in the basics.”
And without any further adieu, let’s understand,
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Process And Mechanism:-
So, remember the Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution is an organic chemical process in which Hydrogen is swiped out or replaced with an electrophile. And to understand it let’s dive deep into the process and mechanism of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution to get a better understanding of this chemical process as it’s not so complicated and it’s easy to understand. So, the electrophilic aromatic process consists of three main fundamentals:-
- During the process, new σ bonds are formed from a C=C in the arene nucleophile.
- Protons are removed during this process by breaking down C-H σ bond.
- Then the C=C is reformed which restores the aromaticity.
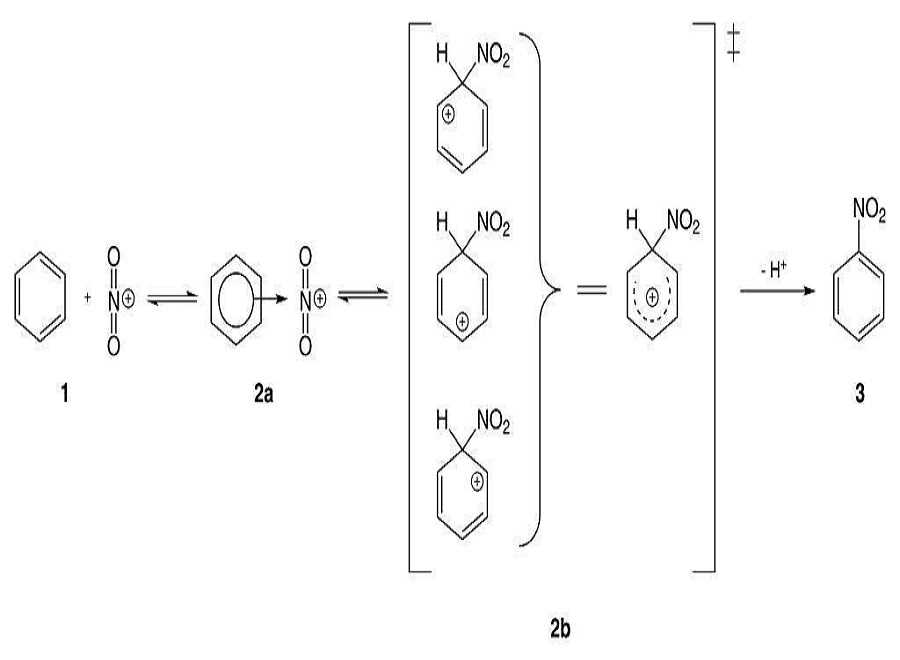
So, to understand the concept of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution easily and further, let us understand the mechanism. The mechanism is a two-step process. So, here is the mechanism of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution:-
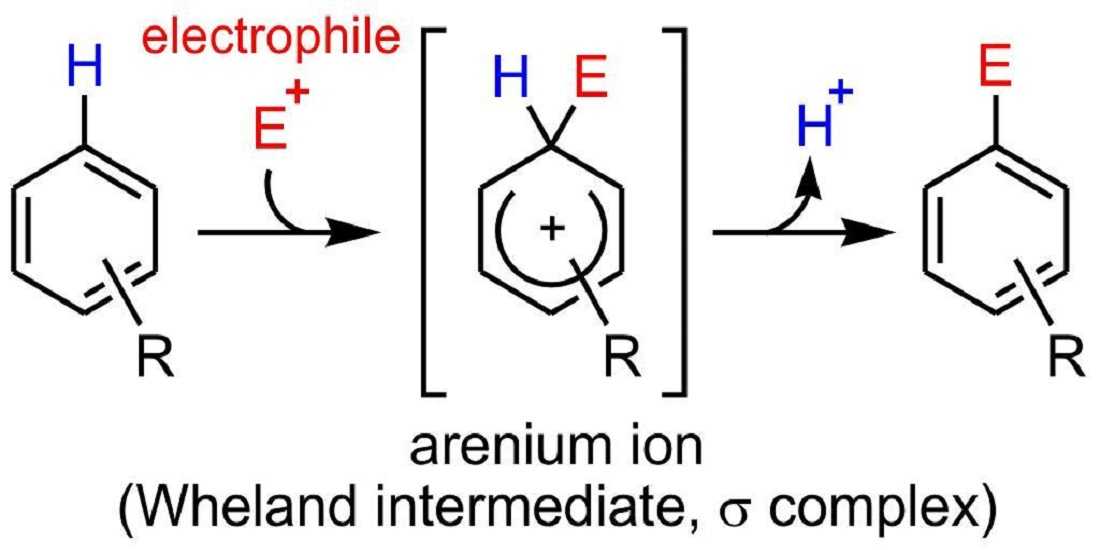
Step 1 :- The Electrophile attacking the pi electrons
The reaction starts when the electrophile attacks the pi electrons in the benzene ring, a base for the Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. And this results in the formation of positively charged and delocalized cyclohexadienyl cation or a resonance-stabilized carbocation known as an arenium ion. The ions formed basically consist of three main resonance contributors and the electrophilic that gets formed generally takes a lot of time and it’s a slow process. In this process further, some changes eventually lead to the loss of aromaticity, as there’s a presence of high energy activation. Also, some other factors result in the loss of aromaticity and the attack of the electrophile and it consists of factors like resonance, probability, and steric hindrance.
Step 2 :- Deprotonation of the arenium ion
In this mechanism step, the arenium ion is deprotonated from a weak base. There is also a formation of carbocation intermediate that is attacked from the weak base that eventually results in the loss of protons. Then what happens is the aromaticity is restored as the protons are used to form a pi bond. This is a fast process and is exergonic. And an important point to note is that the carbocation losses a proton as a result of the electrophile attacking the benzene ring.
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Examples:-
There are two prime examples of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution and they are:-
- Nitration.
- Sulfonation.
So, Nitration is basically derived from Nitronium Ion, and Sulfonation is derived from Sulfur trioxide(SO3) both are electrophiles respectively, and both the electrophiles react differently with benzene to give nitrobenzene and benzenesulfonic acid respectively.
So, let’s understand these two examples with an explanation:-
- Nitration of Benzene:- So, basically the Nitronium Ion is formed through the protonation of nitric acid by sulfuric acid, which leads to the loss of a water molecule and lays the formation of Nitronium Ion.
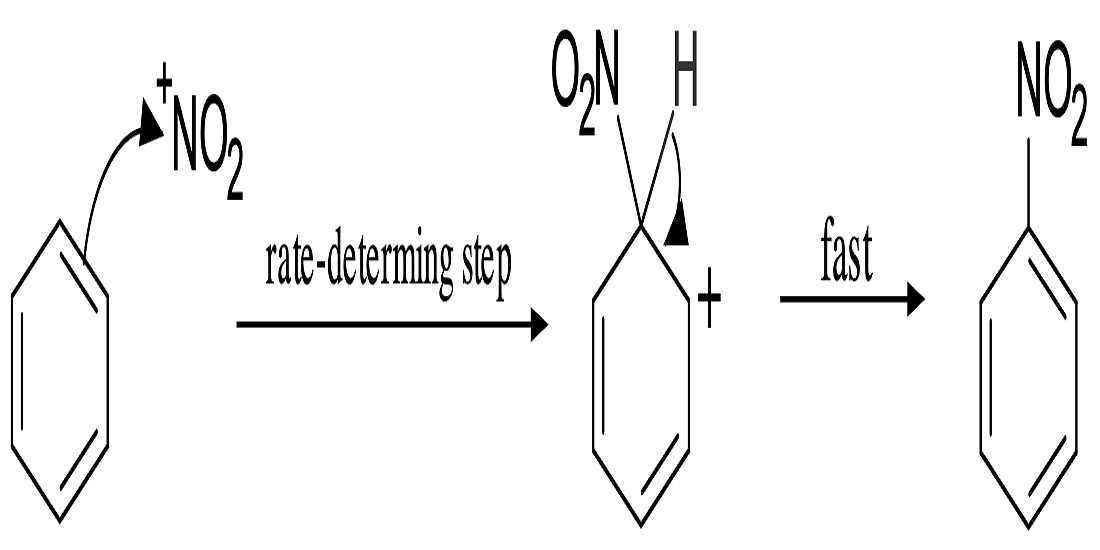
2. Sulfuric acid activation of nitric acid:- The first thing to do in the nitration of benzene is to activate HNO3 with sulfuric acid so that you can produce a stronger electrophile because when the Nitronium Ion reacts with sulfuric acid and since its a good electrophile, it gets attacked by the benzene to produce nitrobenzene.
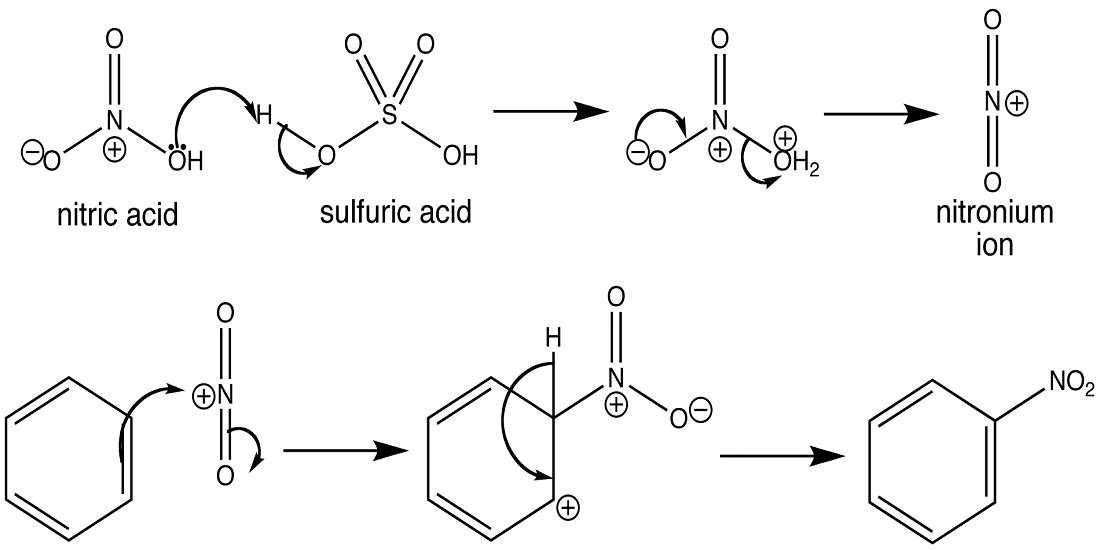
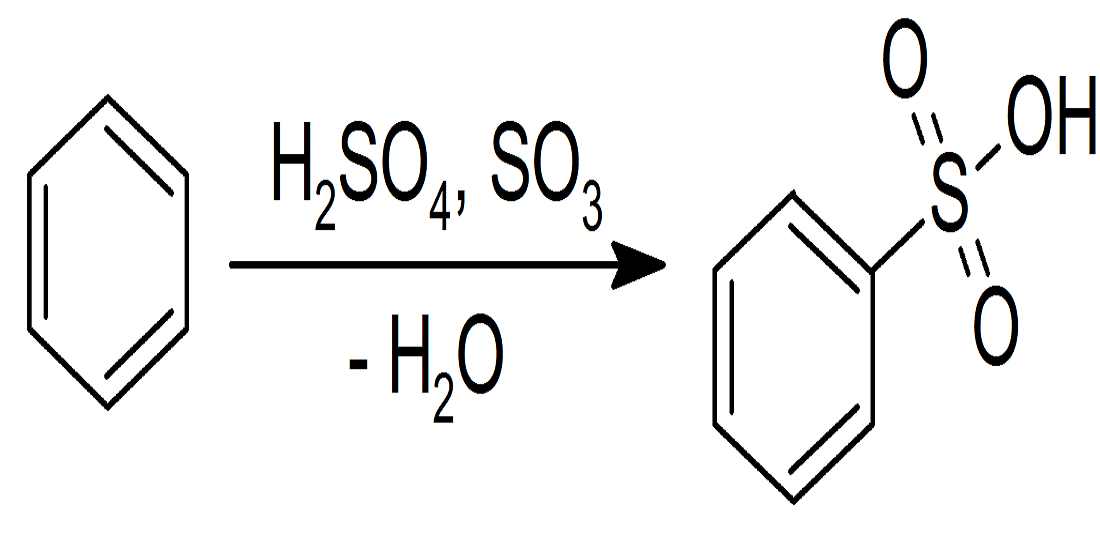
3. Sulfonation of benzene:- Sulfonation leads to the formation of benzenesulfonic acid by adding sulfur trioxide and fuming sulfuric acid. Sulfonation is a reversible reaction, as it can get reversed by adding hot aqueous acid to benzene sulfonic acid to produce benzene. Fuming sulfuric acid also referred to as oleum and is a concentrated solution that consists of dissolved sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid. So, basically, sulfur trioxide is electrophilic because the oxygen pulls the electrons away from it as oxygen is electronegative. And so, the benzene attacks the sulfur to produce benzenesulfonic acid.
Uses Of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution:-
The Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution is one of the most highly used organic chemistry and makes the field of chemistry bigger and better. The Electrophilic Aromatic Substitute can be used for many things from industrial to commercial uses, it’s used to produce:-
- Pharmaceutical products.
- Agrochemical products.
- Industrial products.
- Green Chemistry can be used to protect rubber, natural, or synthetic, from the harmful effects of exposure to the atmosphere and sunlight.
- With the help of benzenesulfonic acid, it can also be used in the synthesis of detergents, dyes, and sulfa drugs.
- And one more important usage of it is Benzenesulfonyl chloride, which is a precursor to sulfonamides, which can be used for chemotherapy.
Also Read: Magic Number – Nuclear Chemistry and Radioactivity
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Resources:-
Well, the internet is a huge place to not only post pictures on social media but also to gain knowledge and learn a new skill. So, readers if you want to know more about Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution, and even if you are not from a Science background and still have an interest in this crazy field as I have, then there’s this pdf where you can learn basics about Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution and also there’s this PPT that has elaborated the basics of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution in a very easy manner, definitely, you should have a glance at it. And if you don’t want to read about it and rather watch the video, then I’ll recommend some really great videos as I have been watching on YouTube,
- Khan Academy’s Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution.
- Professor Dave Explains Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution.
These two videos are just amazing and they have elaborated the concepts of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution very well. So, I highly recommend you guys watch these two videos and read about them, as this topic is interesting.
Conclusion:-
The field of Chemistry is really important as it’s an integral part of Science, no matter, either you are a student or a professional, I think it’s really important to have some basic science knowledge, as the world runs on science, and technology, as it makes you think, makes you excited.
And for people who are currently pursuing science, whether it’s Engineering or Medical, you can’t skip Chemistry as it’ll be an integral part of your first year, I myself pursued Commerce, but some of my friends are engineers and they told me that Chemistry is really an integral part of Engineering and even Physics.
So, no matter what update yourself, get to know the basics of science whether it’s Physics or Chemistry, or even Computer Science, learn the basics, and if you can grasp up the basics very well, then you can even take it to the next well, and who knows can make money out of it. So, questions,
Do you think Chemistry is important? If yes,
Do you know the basics of it?
Let me know in the comment section below.