We use different things in our daily life made from metal. We have studied that the earth’s crust is made up of different minerals embedded in the rocks. Various metals are extracted from these minerals after proper refinement and extraction processes. Every material are made and distributed as Mineral and Energy Resources over the globe.
Minerals and Energy Resources are an indispensable part of our lives. Almost everything we use, from a tiny pin to a towering building or a big ship, all are made from minerals. Human beings have used minerals for their livelihood, decoration, festivities, religious and ceremonial rites in all stages of life development.
I have compiled Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 important Topics and Questions in one single article.
What is a mineral?
Geologists and archeologists define a mineral as a “homogenous, naturally occurring substance which has a pre definable internal structure.” Minerals are found in varied forms in nature, ranging from the hardest diamond to the softest talc. Rocks are combinations of homogeneous and wear & rear processes of substances called minerals.
Occurrences of Minerals:
Minerals are usually found in ores. The term ore is defined as a substance made by the accumulation of minerals and other elements. The mineral content of ore must be sufficient concentration to make its extraction value commercially high. The type of formation or structure in which they are found determines the relative ease with which mineral ores may be mined. This also determines the cost of extraction and cost variance in distribution.
It’s very important for us to understand how and what are the types and modes of occurrences of minerals:
- In igneous and metamorphic rocks, the minerals are found in cracks and crevices.

- In sedimentary rocks, a number of minerals occur in beds or layers. They have been formed as a result of deposition, accumulation, and concentration.
- The decomposition of surface bed rocks and the removal of soluble constituents also form the minerals.
- Certain minerals accumulate in a place and occur as alluvial deposits in sands of valleys and floors in hills. They cannot get corroded by water action.
- The oceanic waters do also contains a vast range and quantity of minerals, but some of them are not economically suitable to be extracted.
Also Read:
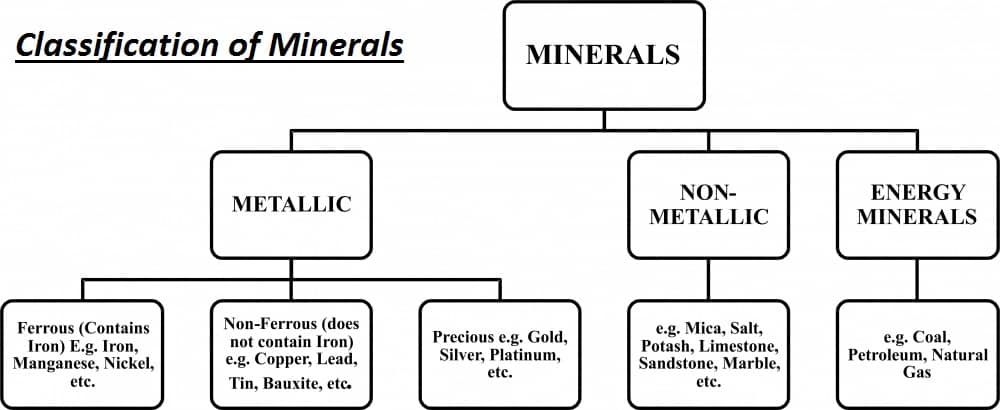
Classification of Minerals and Energy Resources:
India is fortunate to have fairly rich and varied mineral resources. However, these are unevenly distributed. Minerals and Energy Resources are classified on the basis of 3 types:
- Metallic Minerals
- Non- Metallic Minerals
- Energy Resources.
-
Metallic:
Metallic Minerals are classified on the basis of 3 types:
a. Ferrous Minerals:
- They are naturally occurring inorganic substances which contain Fe (iron) as an element in the composition.
- They show high magnetic properties and are mainly composed of iron as hydroxides, carbonates & sulfides.
The types of ferrous minerals are Iron ores, Manganese, nickel, cobalt, etc.
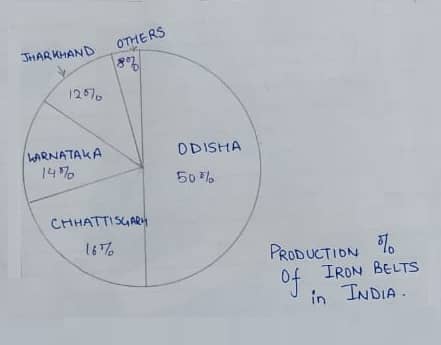
A. iron ores:
- Iron rocks are rocks from which metallic iron is economically extracted. They are actually rich in iron oxides and vary in colors like gray, bright yellow, deep purple, etc.
- Iron ore is the raw material used to make pig iron- 98% of mined iron is used to make steel.
- Magnetite is the finest iron-containing iron up to 70%, & Hematite is important industrial iron ore with 50-60% iron content.
- The major iron belts and its percentage of production are mentioned below:
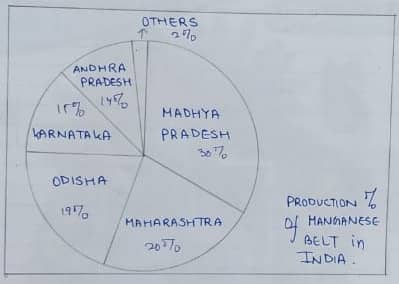
B. Manganese:
- They are a transition metal with a multifaceted usage of industrial alloys & stainless steel.
- It’s used to make steel and Ferro-manganese alloys, bleaching powder, insecticides & paints also.
- The major belts and its percentage of production are given below:
b. Non- Ferrous Minerals:
- They are naturally occurring inorganic substances that do not contain Fe (iron) in it as its element in the composition.
- They are non-magnetic and are composed of various elements in their composition.
The types of non-ferrous minerals are Copper, Zinc, Bauxite, etc.
A. Copper:
- They are malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity.
- They are mainly used in the production of electrical cables, electronics, and chemical industries.
- The Balaghat mines in Madhya Pradesh, Khetri mines in Rajasthan, and Singhbhum district of Jharkhand are leading producers of copper.
B. Bauxite:
- Bauxite deposits are formed by the decomposition of a wide range of rocks rich in aluminium silicates.
- Aluminium is obtained from bauxite. Aluminium has good conductivity and great malleability.
- The deposits are mainly found in the Amarkantak plateau, Maikal hills, and the plateau region of Bilaspur-Katni.
-
Non- Metallic:
The non-metallic minerals are as follows:
A. Mica:
- They are a group of silicate minerals, including basal cleavage. They are monoclinic in nature, pseudohexagonal crystalloid structure.
- They are used in a variety of products manufacture from drywalls, paints to electronics and roofing, etc.
- They are deposited and found mainly in Nagpur districts of Maharashtra, Koderma-Gaya-Hazaribagh belt in Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh.
B. Limestone:
- It’s a carbonate sedimentary rock that is often formed by various geological processes.
- It’s considered to be a rock mineral as its originality is from crystal rock structure.
- It’s mainly composed of calcite & aragonite i.e., CaCO
- They are unevenly spread in Rajasthan- Gujarat- Madhya Pradesh belt, Telangana- Tamil Nadu belt, and Chhattisgarh- Karnataka belt.
-
Energy Resources:
Energy is said to be the capacity to do some work. An energy resource is something that can produce heat, power life, or produce electricity.
There are 2 types of resources:
a. Conventional Energy Resources:
- The resources which have been in use for years and are limited in our nature are called Conventional Energy Resources.
- They are Non- Renewable sources of energy because once got depleted from nature, they won’t be easily made again.
The Conventional sources of energy are:
A. Coal:
- The most abundant fossil fuel found in nature is that they are used to generate power for industries and domestic use.
- India is considered to be the 4th largest coal-producing country, mainly found in Bihar, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Bengal, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, etc.
B. Petroleum:
- A naturally occurring substance, the yellowish-black liquid found in earth’s surface. It consists of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and organic compounds.
- The use of petroleum as fuel is a major cause of global warming & water acidification.
- Areas of Mumbai High, Assam & Gujarat are major petroleum belts in India.
C. Natural Gas:
- Also called fossil gas, naturally occurring hydrocarbon gas, a mixture of methane gases, and other various other gases.
- It’s a non-renewable source of energy, primarily used for heating, cooking, and electricity generation.
- The gradual use and consumption of natural gas is driving our climate and environment towards conservation from degrading.
- They are in the ready phase to replace liquid fuels.
- They are mainly reserved in areas of Krishna- Godavari basin, Mumbai High & Andaman- Nicobar islands.
D. Electricity:
- By burning other fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and gas, we can produce thermal power.
- It’s defined as Thermal Electricity.
b. Non- Conventional Energy Resources:
- The energy sources which are generated with the help of resources available in our nature are called Conventional Energy Resources.
- They are a Renewable energy source because they get never depleted from nature; they are generated again and again.
The types of non- conventional source of energy are:
A. Solar Energy:
- They are produced by Sunlight.
- The photovoltaic cells are exposed to sunlight and electricity is produced.
- They are used for cooking & saving water.
B. Wind Energy:
- They are generated by harnessing the power of the wind.
- One of the biggest wind farms is in Tamil Nadu, Nagarcoil.
- Apart from these, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat do also have wind farms, which are well utilized by the population.
C. Tidal Energy:
- Oceanic tides can be used to generate electricity.
- Floodgate dams are built across inlets. During high tide, water flows into the inlet and gets trapped when the gate is closed.
- After the tide falls outside the flood gate, the water retained by the floodgate flows back to the sea via a pipe that carries it through a power-generating turbine.
- Gulf of Khambat, Gulf of Kucch & Gangetic delta are major producers of tidal energy.
D. Biogas:
- In rural areas, human, plant & animal wastes are collected and decomposed to form biogas for domestic consumptions.
- Various Gobar Gas Plants are set up in rural areas by the govt. in order to help people to produce biogas and live a healthy and needful life.
- It prevents using dung cakes & burn coal, thus preventing pollution and degradation of the environment.
Also Read: Difference between conventional and non-conventional sources of energy.
Conservation of Minerals and Energy Resources:

Minerals and Energy Resources are there in nature for the sake of our users only. But using it rigorously and without nay, prevention would lead to depletion of these sources and degrade the value of our future generation.
The points to be remembered while the use of these and conservation steps are:
- Using in a planned and sustainable manner.
- Using alternative renewable substitutes.
- Improvising technologies for profitable extraction.
- By incorporating 3 R’s of conservation- Reduce, Reuse & Recycle.
- Using public transport systems in place of individual vehicles.
- Switching off lights when not in use.
- Using power saving devices.
- To find out new innovations and areas of using minerals and energy resources.
Conclusion:
Minerals and Energy Resources are widely and unevenly spread all over the world, which are vigorously and disassociate used by us. Soon all the resources would get depleted and will result in no energy source to generate energy. There is a need of hour to make aware and stop the unwanted use of resources by humans. All the natural calamities and disasters are the result of unthinkable use of resources.
Here I made a short note Mineral and Energy Resources class 10 with all important questions and areas to be remembered.
Frequently Asked Question:
Q1. What are the advantages of a Conventional source of energy?
Ans: The efficiency of energy sources is high. The production cost is low.
Q2. What are the disadvantages of Conventional source of energy?
Ans: It is not environment friendly, i.e., it has polluting nature. After a long run, it will be depleted soon.
Q3. What is the importance of a Non-Conventional source of energy?
Ans: They are renewable, pollution, free, abundant availability, and eco-friendly.
Q4. What are the major belts and areas of iron ores?
Ans: Odisha- Jharkhand belt, Durg- Bastar- Chandrapur belt, Ballari- Chikkamagaluru- Karnataka belt , Maharashtra- Goa belt
Q5. What is the difference between an ore and a mineral?
Ans: Minerals are extracted from the earth’s crust by mining, whereas ores are minerals that are profitably extracted. All ores are minerals, but all minerals are not ores.

Great Information…
Awesome job…