In this world of web and Networking, we can’t tend to imagine our lives without the web. Networking could be a part of the web that manages the network. It’s, therefore, necessary for us in today’s world. One will perpetually notice solutions to answers/problems. It’s therefore convenient and simple to search out answers on the web with one click. In this article, we tend to share Networking Interview Questions and Answers.
Earlier, we’ve to travel by the books to search out the answers and browse nearly the whole book to search out that one answer. If you have got to organize for an interview than it had been a busy job to browse 5-6 books earlier however currently it’s simply a matter of seconds, and you may get all the answers to your queries. Hence prep for the interview became so much painless.
So, here are some questions listed down which are usually asked in the Networking Interview Questions and Answers with a visual illustration to form you perceive the questions simply. This may assist you to strive and convey success to your career. I actually have listed 4o of them.
Networking Interview Questions and Answers
1.What is a Topology? Make a Case for different kinds of Topology?
The topology could be a layout of the PC network, and it outlines however the computers, devices, cables are connected.
Network topologies are classified as below:
a) Bus Topology: In Bus Topology, all the devices of the network are connected to one cable (also known as the backbone). As all the devices are connected to a similar cable, it’s termed as Bus Topology.
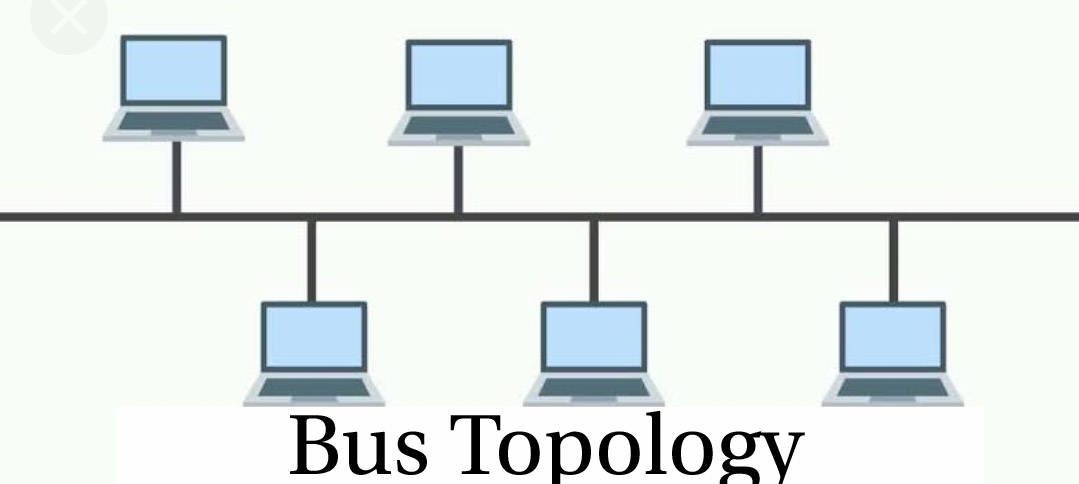
The advantage of bus topology is it’s terribly simple to put in. And therefore the disadvantage is that if the cable breaks then the entire network are disconnected.
b) Star Topology: In Star Topology, there’s a central controller or hub to which each device is connected through a cable. During this topology, the devices aren’t connected to every different device.
If a tool has to communicate with the opposite, then it’s to send the signal /data to the central hub. Then the hub sends a similar knowledge to the destination.
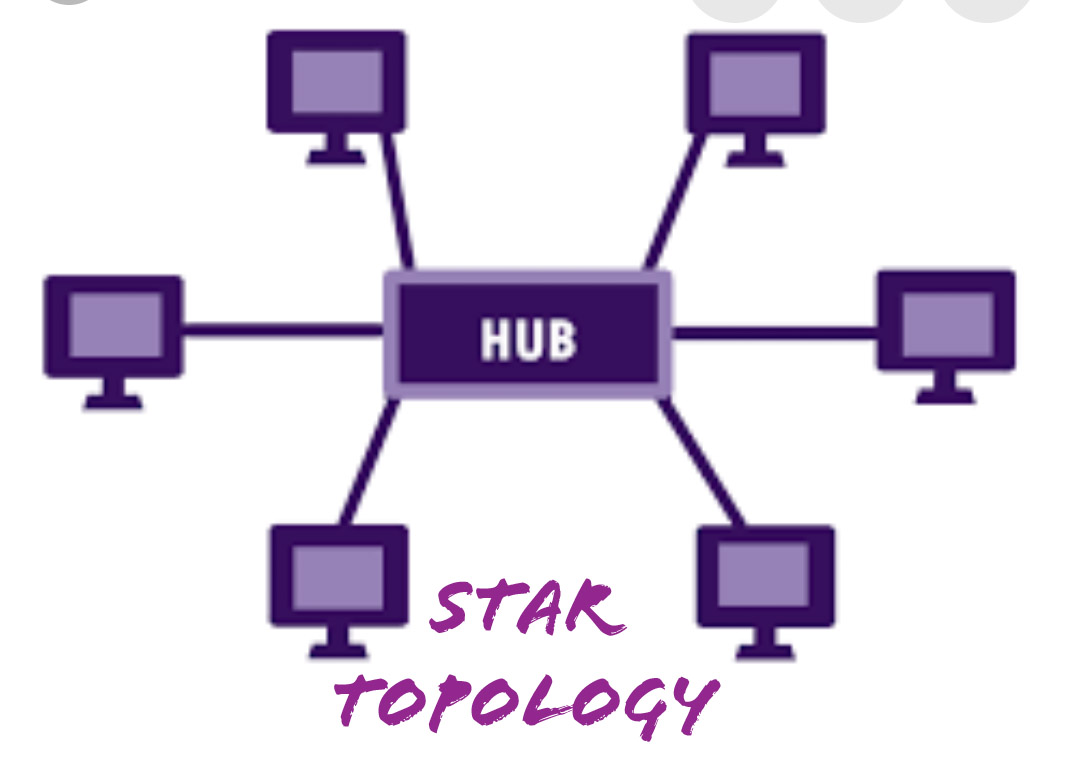
The advantage of the star topology is that if one link breaks then solely that one specific link is affected. The entire network remains undisturbed and unchanged.
The main disadvantage of the star topology is that every device of the network is obsessed on one hub. If the central hub gets unsuccessful, then the entire network gets disconnected.
Also Read: Difference between C and C++ – Basic Differences
c) Ring Topology: Each device of the network is connected to 2 additional devices on either facet, that successively forms a loop.
Data / Signal in Ring topology flows solely in a very simplex from one device to different and reaches the destination node.
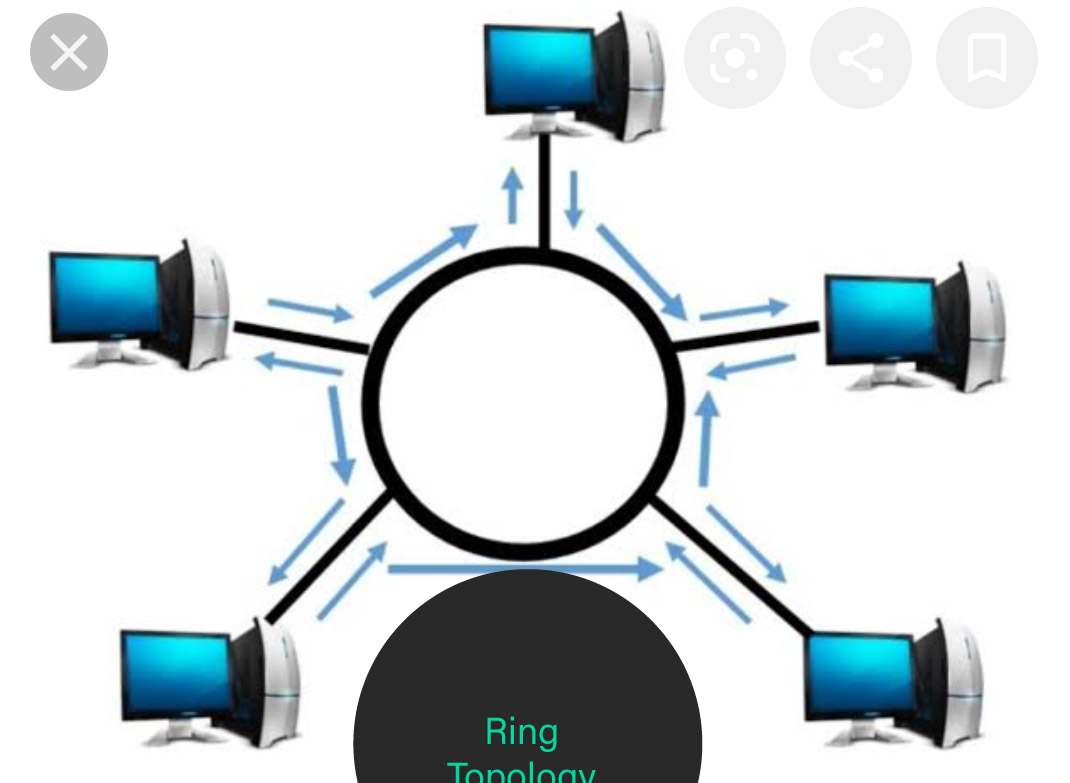
The advantage of ring topology is that it is put in terribly simply. Adding or deleting devices to the network is additionally terribly straightforward.
The sole disadvantage of Ring topology is that the information flows only in one direction. And an opening at a node within the network will have an effect on the entire network.
d) Mesh Topology: During this, each device of the network is connected to any or all different devices of the network.
The advantage of mesh topology is that if one link breaks, then it does not have an effect on the entire network.
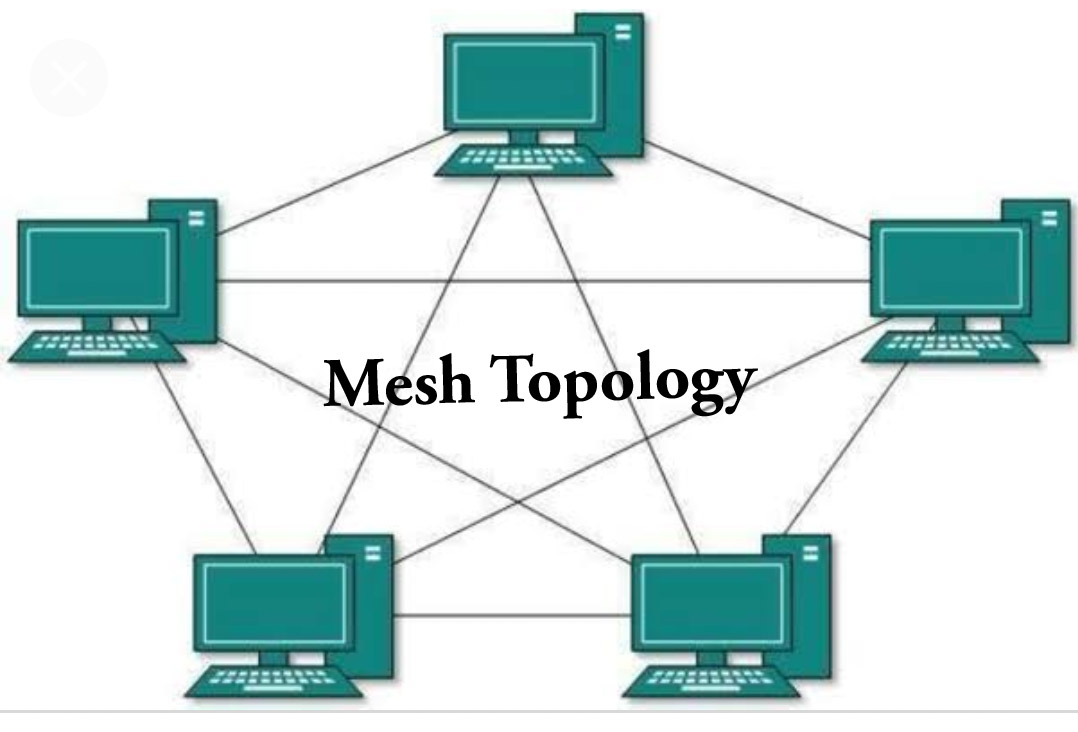
The disadvantage is big cabling is needed, and it’s quite high-ticket.
e) Tree Topology: could be a mixture of star and bus topology. It’s an elaborate version of Star Topology. In this, all the networks are connected to one bus.
The advantages of this network are that one link is broken no impact is there on the other link.
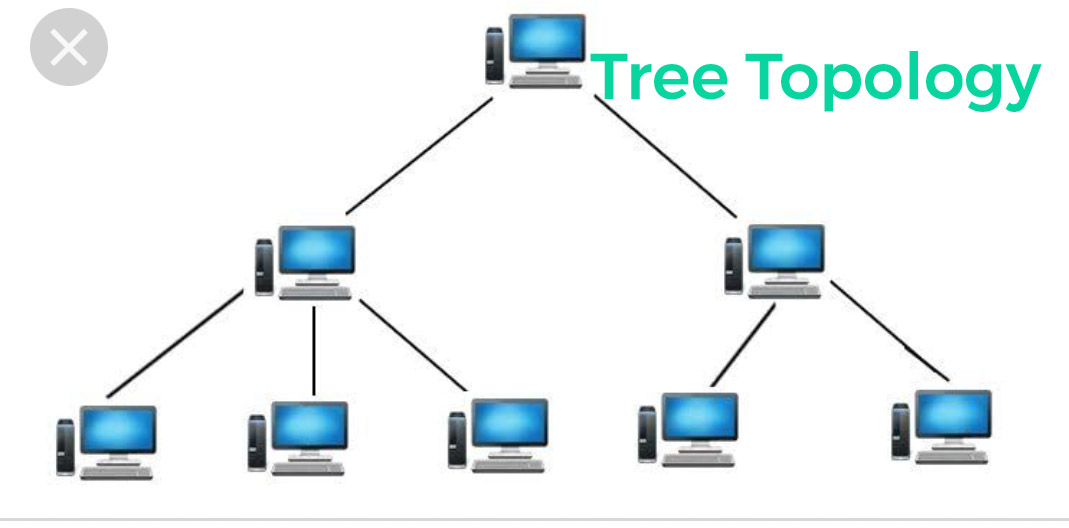
The disadvantage is that if the main bus gets damage, then the entire network gets disconnected.
2.What are OSI Models?
OSI model suggests that Open System Interconnection. It’s a reference model that describes however totally different applications can communicate with one another within the network.
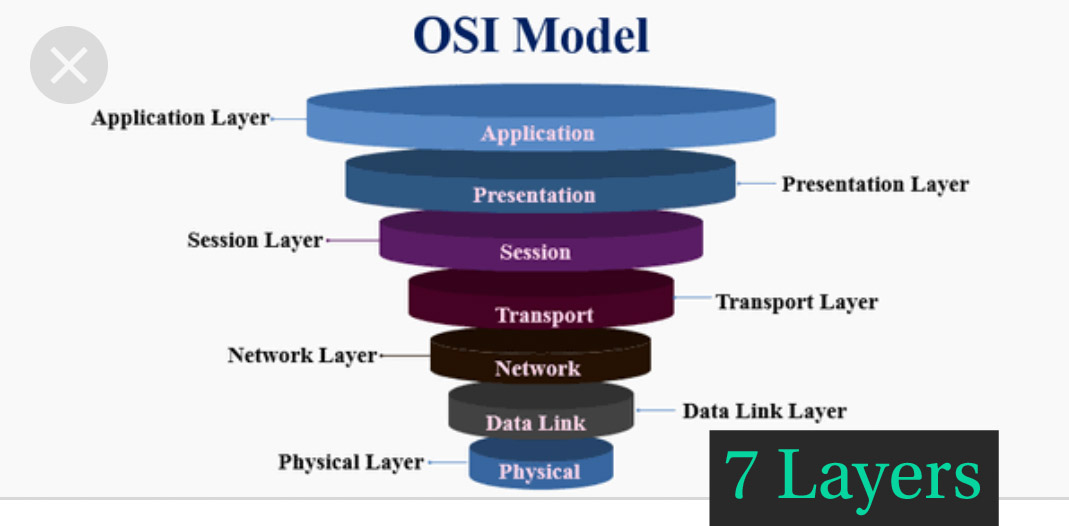
3. What are the various levels of the OSI Model?
There are seven levels of the OSI model:
a) Physical Layer (Layer 1): It converts knowledge bits into electrical impulses.Example: Ethernet.
b) Data Link Layer (Layer 2): During this knowledge, packets are encoded and decoded into bits, and it provides a node to node knowledge transfer. This layer additionally helps find the errors that occurred at Physical Layer.
c) Network Layer (Layer 3): This layer transfers knowledge from one node to a different node within the same network. This variable-length knowledge sequence is additionally known as “Datagrams”.
d) Transport Layer (Layer 4): It transfers knowledge between totally different nodes and provides acknowledgement of palmy knowledge transmission. It helps in keeps track of transmission and sends the segments once more if the transmission fails.
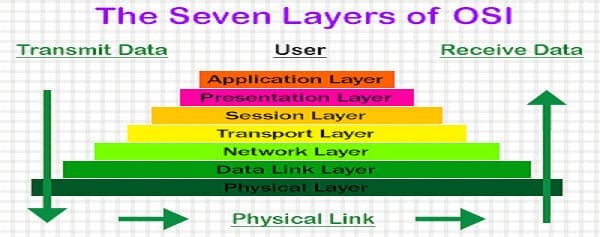
e) Session Layer (Layer 5): The Session layer manages and controls the connections between 2 computers. It establishes, coordinates, exchange and terminates the connections between native and remote applications.
f) Presentation Layer (Layer 6): It’s additionally called as “Syntax Layer”. This Layer transforms the information into the shape during which the application layer accepts.
g) Application Layer (Layer 7): It’s the last layer of the OSI Reference Model and is that the one that’s about to the end-user. Each end-user and application layer interacts with the code application. This layer provides services for email, file transfer, etc.
4.What are Nodes?
A network could be an association set up of 2 or additional computers directly connected by some physical mediums like optical fibre / coaxial cable used for sending, receiving and forwarding the knowledge service and therefore the computers that it’s connected to are called as nodes.
5.What are IP Addresses?
It is a unique 32-bit software address in a computer system.
6.What does one mean by TCP/IP?
TCP suggests that Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. It’s a group of protocol layers that’s designed for exchanging knowledge on styles of networks.

7. What does one mean by NIC?
NIC stands for Network Interface Card. It’s a card that is hooked up to the PC to connect to a network.
Every NIC has its own MAC address which identifies the PC on the network.
It provides a wireless connection to a LAN.NICs were used on a desktop computer.
8.What does one mean by Firewall?
It is a security system that’s accustomed to defending computer networks from unauthorised access.

9.What is Network? Justify different kinds of Network?
The network is outlined as a group of devices connected to employing a physical transmission medium. Based on the size of the network, they are categorised as below.
Personal Area Network(PAN): A personal area network, or PAN, is a computer network that is for an individual.
Local Area Network (LAN): A network with a minimum of 2 computers inside the associate workplace or a similar building is termed as LAN. Generally, it works for one place where individuals can share resources like printers, data storage, etc.
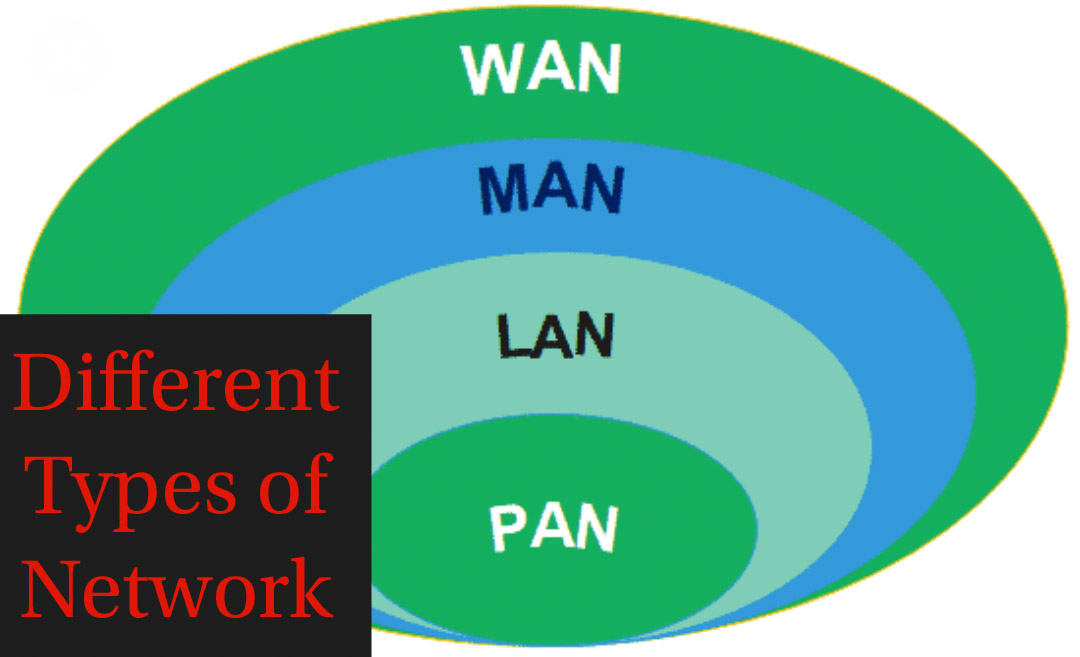
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): It’s larger than LAN and can connect numerous LANs across tiny regions, a city, campus of colleges or universities, etc. that forms a much bigger network.
Wide Area Network (WAN): Multiple LANs and MAN’s are connected to create a WAN. It covers a wider variety of areas like a whole country or world.
10.What does one mean by Anonymous FTP?
Anonymous FTP suggests that to grant users access to files during a public server domain. Users who are allowed access to knowledge in these servers don’t have to be compelled to establish themselves, however instead, need to log in as an associate anonymous guest.
11.What are the main components of Protocols?
Below are the 3 main components of the protocol:
Syntax: It’s the format of the info. This implies within the order the info is displayed.
Semantics: It describes the meaning of the bits in every section.
Timing: It suggests at what time the info is to be sent and how quick it is to be sent.
Also Read: Best differences between RDBMS and DBMS
12.What is POP3?
It stands for Post Office Protocol version 3. It is responsible for accessing the mail service on a client machine. POP3 works on 2 models, like in Delete mode and Keep mode.
13.What does one mean by MAC Address?
MAC stands for Media Access Control. It is the address of the device at the Media Access Control Layer of Network Layout. It’s a unique address which implies that no 2 devices will have the same MAC addresses.
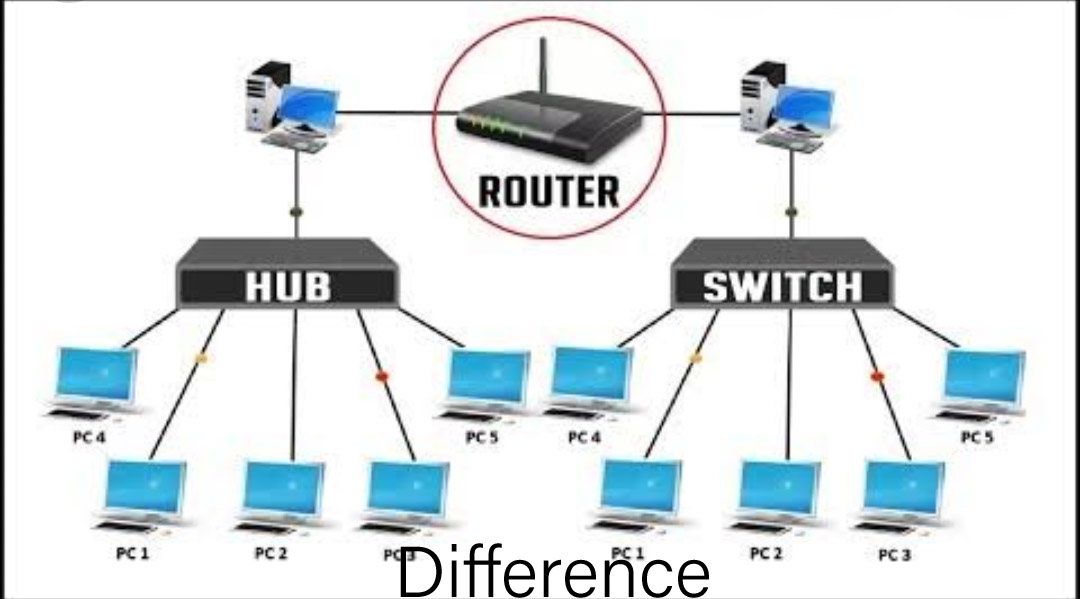
14.Give the distinction between Hub, Switch, and Router?
Hub: will broadcast all knowledge to each port. It has a standard connection point for all the devices.
Switch: It will produce a dynamic connection and supply info to the requesting port.
Router: is that the device which will be responsible for forwarding knowledge packets.
15.What are Unicasting, Anycasting, Multicasting and Broadcasting?
Unicasting: knowledge is sent from one computer to another computer. There’s one sender and receiver.
Anycasting: It’s a network addressing and routing methodology during which datagrams from one sender are routed to the topologically nearest node during a cluster of potential receivers.
Multicasting: may be a form of communication wherever multicast traffic is addressed for a bunch of devices on the network. Here there are one sender and plenty receivers.
Broadcasting: may be a form of communication where knowledge is sent from one computer only one time, and a copy of that data will be forwarded to all the opposite devices.
16.What are Netstat?
It is a type of command which shows network status and protocol statistics(both for incoming & outgoing)
17.What is sneakernet?
It is an informal term used generally to transmit information physically like in a floppy disk, hard drive, USB Cable etc.
18. What’s the distinction between TCP and UDP?
TCP UDP
| It is a communication protocol, in which the data is transmitted between systems over the network.
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. |
In this, the data will be sent continuously, irrespective of the issues in the receiving end.
UDP is a connectionless protocol. |
| TCP is slower than UDP. | UDP is faster than TCP. |
| Heavyweight connection | Lightweight connection |
| Retransmission of packets is possible in TCP. | Retransmission of packets is not possible in UDP. |
19.What are the important differences between MAC address and IP address?
IP MAC
| IP address means internet protocol Address. | MAC Address means Media Access Control Address. |
| It is of 6 bytes. | It is 4 bytes or 16 bytes. |
| It is the physical address of the computer. | It is the logical address of the computer. |
| It operates in the data layer | It operates in a network layer. |
| Can’t be found easily by the third party | Can be found by a third party. |
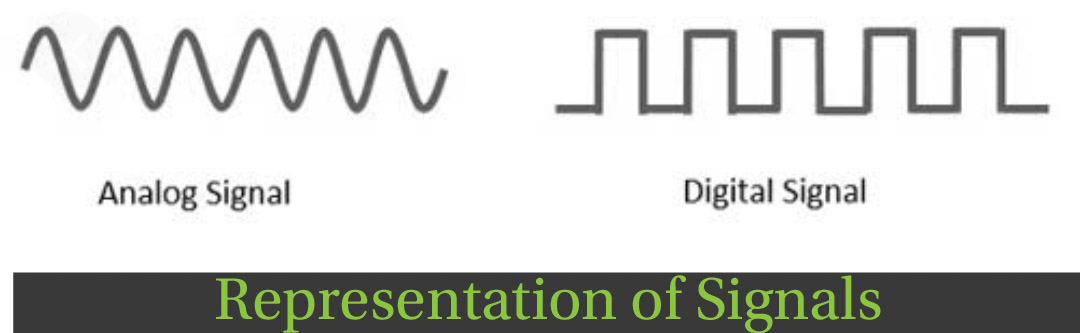
20.What are the differences between analogue and digital signal?
Analog Digital
| Continuous Signals | Discrete Signals |
| Represented by sine waves. | Represented by square waves. |
| A continuous range of values. | Discontinuous Waves |
| Only used in analogue devices. | Suited for digital devices like computers, mobiles etc |
| Record sound wave as it is | Converts the Waves into a binary waveform |
21.What is ipconfig?
Internet Protocol Configuration(ipconfig) that has the ability to gather all the data from IP and then display that data on the screen.
22.What is ICMP?
It stands for Internet Message Control Protocol. Its function is to check whether the data is reaching its destination timely or not. It is used for diagnosing network issues.
23.What is the Peer-Peer Process?
It is a network of personal computers, each of which acts as both server and client so that they can exchange files with each other. It eases the workload by grouping them into peers.
24.What is DHCP?
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) may be a network management protocol used to automate the method of configuring devices on IP networks, so permitting them to use network services.
25.What is VPN?
Stands for Virtual Private Network. It permits us to create online networks & anonymity by making a non-public network from a public one.
26.What is Data Encapsulation?
It is a method of mixing information and functions in every unit known as class. One of the popular features of Object-Oriented Programming(OOPs).
27.What are the links?
Known by the name Hyperlink, that’s a reference of knowledge that users will follow up by clicking or just tapping on it. Hypertexts are usually found with Hyperlinks.
28.What is a client /server network?
A network within which one powerful computer called a server is connected to any or all the opposite networks known as clients is connected.
29.What is TELNET?
A terminal emulation that allows a user to attach to a remote host using a telnet client, usually over port twenty-three.
30.What is half-duplex?
A way of communication between two devices. Here the data flow bi-directional. An example of a half-duplex is a walkie-talkie.
31.What is a full-duplex?
A method of communication between two devices and the data flow is bi-directional too, but the flow is continuous. Example – telephone
32.What do you mean by ASCII?
American Standard Code For Information Interchange.
33.What is ifconfig?
It is an acronym for Interface Configuration and is used on Linux, Mac operating systems.
34.What do you mean by semantic gap?
When the message is sent to the receiver from the sender, he/she may misinterpret it, so then there is a Semantic Gap, and the message is not transmitted. It is one of the communication barriers.
35.What are the Triggers?
Triggers are event-driven specialized procedures and are managed by Database Management Systems(DBMS). They are capable of performing complex actions and using the procedural languages full throttle.
36.What is SNMP?
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a type for different devices on a network to share information. It allows devices to communicate even between hardware and software.
37.What is IDEA?
International Data Encryption Algorithm (IDEA), originally called Improved Proposed Encryption Standard (IPES), is a symmetric-key block cypher.
38.Explain Brouter?
Brouter is a combination of a bridge and a router.
39.What do you mean by encryption and decryption?
Encryption is the process of converting plaintext into a Ciphertext. Whereas Decryption is the process of converting Ciphertext into its original form Plaintext.
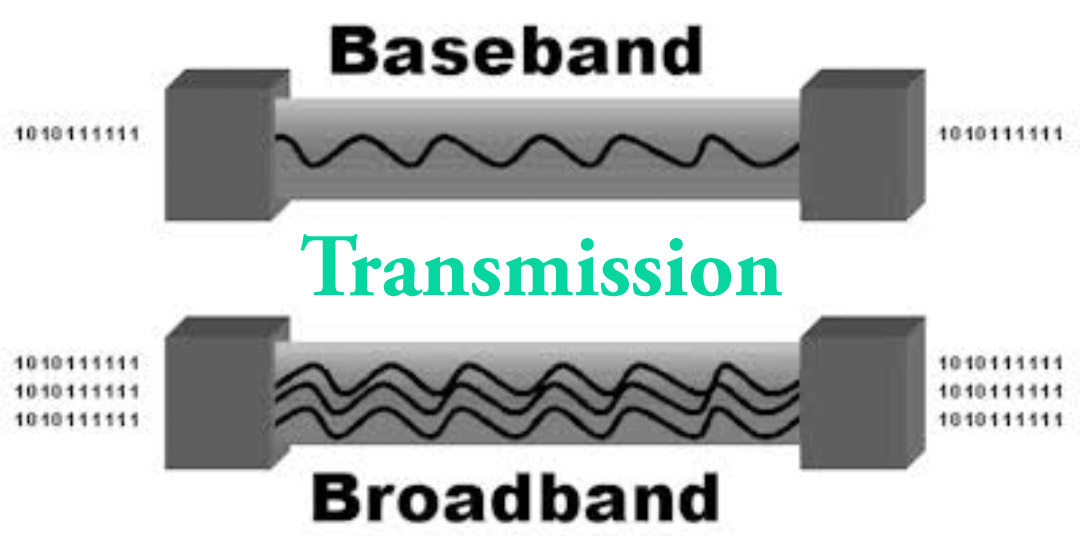
40.Explain the difference between Baseband and Broadband transmission?
In baseband transmission, one signal takes the entire bandwidth of the channel to send data. In contrast, in broadband transmission, many signals with multiple frequencies send data through a single channel simultaneously.
Baseband transmission sends only one signal at a time, and it uses digital signals, whereas Broadband transmission sends multiple signals at a time, and it uses analogue signals.
These are some of the questions which might come in your Networking Interview Questions and Answers. I hope that it may be helpful for you and let you clear your Interview. I hope that I have covered almost all the important questions that might be asked in your Networking Interview Questions and Answers.
Good luck with your exams!!!!!!
—By Ankita Francis
Thanks for this article, i got good knowledge from this, keep it up and please write more articles like this,thank you
Very nicely written…the details are very clear and helpful..great job done by the writer..
Wow .Gud work dear .written well on a very gud informative topic .keep up the work