A new danger to the climate change is on the rise because of the Methane gas leak. Antarctica seabeds have been identified as a potential source of enormous amounts of Methane years ago. But this is the first time that the dangerous global warming gas has been found by the Divers saturating or leaking out of the Antarctica Sea Bed. It is believed that the methane gas has now been released in the atmosphere.
What is the Antarctica Methane gas leak about?
Specialists who had previously estimated about the methane gas leak had trusted methane-devouring microorganisms in the water would consume the gas and control the release of Methane.
But the latest findings archiving the leak found out that these microbes dodged the consumption of the Methane gas for over five years. Even after that, these microbes did not consume the gas completely. This is another negative sign for environmental change, as the speed at which these microorganisms consume the gas could be basic in restricting the global warming.
Because of the delay in microbial colonization, it is practically believed that the methane has been discharged into the air, researchers said. The micro organisms can now be seen at the site of the 10-feet long leakage as white deposits on the Ross sea bed, the sea where the leak has been identified.
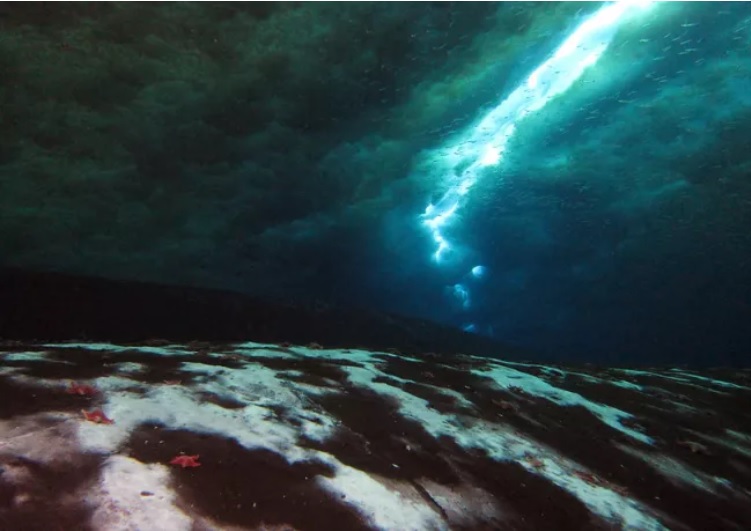

The Seabed of Ross sea where methane-eating microbes are spotted as white deposits.
Why is methane gas dangerous?
Methane, also called a Fossil gas, is a highly contributing greenhouse gas. It absorbs almost 30 times more heat as absorbed by the same amount of Carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide is the largest contributor among all greenhouse gases because it is present in higher amounts and can remain for longer duration in the atmosphere. But if the amount of a way more dangerous gas increases in the atmosphere, the global warming will increase at a deadly speed.
It is speculated by the researchers and scientists that the ancient algae deposits are the original source of the methane dwelling under those seabeds, but the source and cause of this leak is still a mystery.
Why is the Antarctica methane gas leak alarming?
Methane can escape into the atmosphere from different natural and artificial sources like fossil fuels, wetlands, gas hydrates under the seabed, production and transportation of coal, natural gas and oil, other factories and industrial activities, agricultural activities and fields like rice paddy fields and decay of organic waste in landfills.
An enormous amount of Methane gas remains stored under the oceans, and Antarctica is evaluated to contain approximately one quarter of the total marine methane.
The methane gas leak from frozen seabeds of Antarctica might mean that the effect of global warming has become inevitable. What caused the gas to escape out of the Ross seabed is unknown, but the researchers say that it is not because of the warming of the waters of the Ross Sea, because the sea has not yet warmed crucially for such conclusion.
‘The delay in methane consumption is the most important finding.” lead researcher Andrew Thurber, from Oregon State University, told The Guardian. There was a net positive output of around 16million tonnes of Methane over the years, but most climate models have not accounted this delay in the microbial consumption of leaking methane to predict the extent of future climate emergencies.
“The effects of underwater methane gas leak remain poorly studied, especially in the inhospitable environment of Antarctic area because they’re hard to find.” Thurber said.
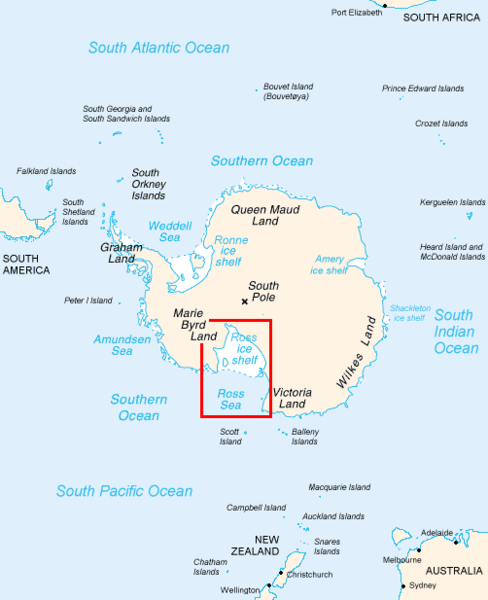
The site of the Methane leak: Ross sea, Antarctica.
The findings of the Antarctica Methane gas leak were published in a journal called the ‘Proceedings of the Royal Society B’ on Wednesday, 22 July 2020.