Introduction
DNA Fingerprinting is a process used to find out the characteristics of the DNA of an individual. DNA profiling is a measurable method in criminal examinations, contrasting criminal presumes’ profiles with DNA proof in order to survey the probability of their inclusion in the wrongdoing. DNA profiling has additionally been utilized in the investigation of the creature and plant populaces in the fields of zoology, herbal science, and agribusiness. DNA examination expected to recognize an animal variety, as opposed to an individual, is called DNA barcoding.
Also, view: Top 10 Longest Bone in the Human Body
Principle

Development of DNA
In the United States of America, the DNA Identification Act of 1994 approved the Federal Bureau of Investigation to grow a pilot venture into a national DNA database, the Combined DNA Index System (CODIS), as an apparatus for comprehending vicious violations. CODIS joins DNA examination with PC innovation to empower wrongdoing research facilities at the neighbourhood, state, and national levels to trade and look at DNA profiles electronically. The database involves two lists: the Forensic Index, which contains DNA profiles from wrongdoing scene proof, and the Offender Index, which contains profiles from those sentenced for lawful offence sex offences and other vicious violations.
Applications
- Forensic Science
- Paternity and Maternity Determination
- Personal Identification
- Diagnosis of Inherited Disorders
- Development of Cures for Inherited Disorders
- Detection of AIDS
- Breeding Program
Forensic Science
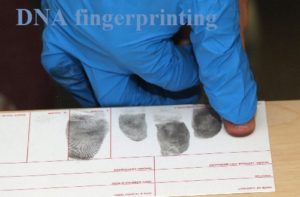
They are widely used in the field of criminal investigation and Forensic science is the application of science to criminal and Forensic scientists collect, preserve, and analyze scientific evidence during the course of an investigation. While some forensic scientists travel to the scene of the crime to collect the evidence themselves, others occupy a laboratory role, performing analysis on objects brought to them by other individuals. This helps the investigation process to get close easily without any confusion.
Paternity and Maternity Determination
This Test can likewise decide the probability of somebody being an organic grandparent. DNA paternity testing is the utilization of DNA profiles to decide if an individual is the organic parent of another person. It can be particularly significant when the rights and obligations of the dad are in issue and a youngster’s paternity is in question.
Personal Identification
Personal identification is made easy by the development of DNA as the victim is being tested in order to find out they are the cause for the case.
Diagnosis of Inherited Disorders
All ailments have a hereditary part. Changes might be acquired or created in light of ecological anxieties, for example, infections or poisons. A definitive objective is to utilize this data to treat, fix, or, if conceivable, forestall the improvement of infection.
Development of Cures for Inherited Disorders
By considering the DNA fingerprints of family members who have a background marked by some specific issue, DNA models related to the sickness can be learned.
Detection of AIDS
These advancements helped to identify the genetic transformation of the disease of AIDS. This helps to identify a person who is being suffered from the disease and helps to treat them properly and prevents the spreading of the disease.
Breeding Program
Raisers expectedly utilize the phenotype to assess the genotype of a plant or an animal. As it is hard to make out homozygous or heterozygous strength from appearance, the DNA fingerprinting permits a picky and exact assurance of genotype.
Conclusion
The advancement in this field has a great impact and benefits in the field of science and criminal investigation. This also witnesses the tracking of genetic diseases.
2 thoughts on “What is DNA Fingerprinting-principle, development & its best application”